Trauma & Fracture
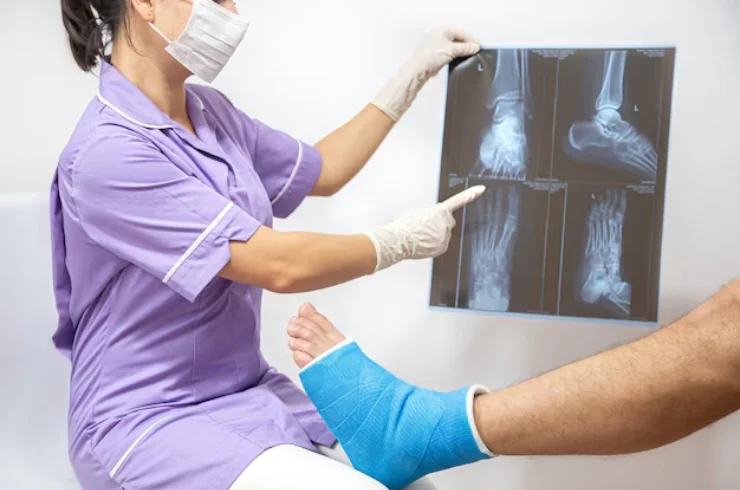
Trauma and fractures refer to injuries that involve damage to bones and surrounding tissues, often resulting from accidents, falls, or direct impacts. These injuries can range from minor fractures to complex, life-threatening situations requiring immediate medical intervention.
Fractures are classified based on the type of bone break and the location:
- Closed fractures: The bone breaks but does not puncture the skin.
- Open fractures: The bone breaks and protrudes through the skin, increasing the risk of infection.
- Comminuted fractures: The bone breaks into multiple fragments.
- Greenstick fractures: Incomplete fractures common in children, where the bone bends but doesn’t break fully.
Trauma refers to injuries that affect not just the bones, but also muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints. Trauma may involve:
- Soft tissue injuries, such as sprains and strains.
- Dislocations, where bones are forced out of their normal position in a joint.
- Contusions or bruises, which involve damage to the underlying tissue without breaking the skin.
Management of trauma and fractures typically involves:
- Immobilization: Using splints, casts, or braces to stabilize the affected area.
- Surgical intervention: Required for severe fractures, including open fractures, displaced fractures, or fractures involving joint structures.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy helps restore function and strength after recovery.